-
Mail us
contact@tiger-transformer.com -
Phone us
(+86)15655168738
Mail us
contact@tiger-transformer.comPhone us
(+86)15655168738An inverter is a small circuit that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). The battery's power is converted into "mains voltage" or AC power. This power supply can be used in electronic devices such as televisions, mobile phones, and computers. The main function of the inverter is to convert DC power into AC power and the step-up transformer is used to generate the main voltage from the generated AC power.
Inverter block diagram:
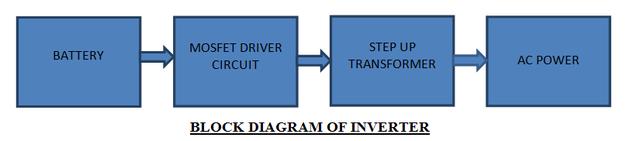
Main components:
CD4047: CD4047 was designed in Texas Very low power multivibrator INSTRUMENTS.it can work in monostable multivibrator or in astable multivibrator mode, it can work in free running or heatable mode and Also provides good astable frequency stability. It can generate a 50% duty cycle, which will produce a pulse that can be used in an inverter circuit. This is mainly used for frequency discriminators, timing circuit frequency division, etc.
IRF540: IRF540 is an N-channel enhancement mode silicon gate field effect transistor (MOSFET), mainly used in switching regulators, Switching converters, relay drivers, etc. The reason for using them in inverter circuits is because it is a high switching transistor that can operate at very low gate drive power and has high input impedance.
IRF540 symbol:

Simple 100W inverter circuit diagram:

Explanation:
In the circuit diagram we can observe that the 12V battery is the connector of the diode LED and is also connected to pin 4047 of IC8 which is the VCC or power pin and is also connected to pin 4 and 5. They are unstable and the complement of IC is unstable. The diodes in the circuit will help not create any reverse current and the LED will act as an indicator of whether the battery is working.
ICCD4047 will operate in astable multivibrator mode. To operate in astable multivibrator mode we need an external capacitor which should be connected between pin 1 and pin 3. Pin2 is connected by a resistor and a variable resistor to change the output frequency of the IC. The remaining pins are connected to ground. Pins 10 and 11 are connected to the gate of the MOSFETIRF540. Pins 10 and 11 are Q and ~Q, the output frequency from these pins is generated at 50% duty cycle.
The output frequency is connected to the MOSFET through a resistor, this will help prevent loading of the MOSFET. The main AC current is generated by two mosfets which will act as two electronic switches. The battery current flows through Q1 through the upper or positive half of the transformer's primary coil, this is done when pin 10 goes high and the lower or negative half passes the opposite current through the transformer's primary coil, which is This is done when pin 11 is high. Current is generated by switching two MOSFETs.
This AC power is given from this coil to the step-up transformer of the secondary coil, only we will get the increased AC voltage, this AC voltage is too high; from the step-up transformer, we will get the maximum voltage. Zenor diodes will help avoid reverse current flow.
Note: The AC generated is not equal to normal AC mains or house holding current. You cannot use this voltage with pure appliances such as heaters, rice cookers, etc. Since heat dissipation from the MOSFET's rapid switching affects efficiency, use a heat sink to eliminate this problem.