-
Mail us
contact@tiger-transformer.com -
Phone us
(+86)15655168738
Mail us
contact@tiger-transformer.comPhone us
(+86)15655168738Almost 9°% of the electrical energy we use in daily life comes from AC energy. Be it our home appliances, office equipment or industrial machines, we all use AC power to power these devices.
If you are a beginner, alternating current or simply alternating current is a type of electricity in which the current changes periodically in both magnitude and direction. In addition, depending on the application, AC power can be used as a single-phase or three-phase system.
A single-phase AC power system consists of two conductors called phase (sometimes called line or live or hot) and neutral. With a three-phase system, you use three or four wires to transmit power (there is no neutral in a three-wire three-phase power supply, all three wires are phases).
Now let us take a closer look at single-phase and three-phase systems and understand the differences between single-phase and three-phase power supplies.
What is single-phase power supply?
As mentioned earlier, in single-phase power supply, only two wires called phase and neutral are used to distribute the power. Since AC power has a sine wave shape, the voltage peak in single phase power is 9°° during the positive cycle and again at 27°° during the negative cycle.
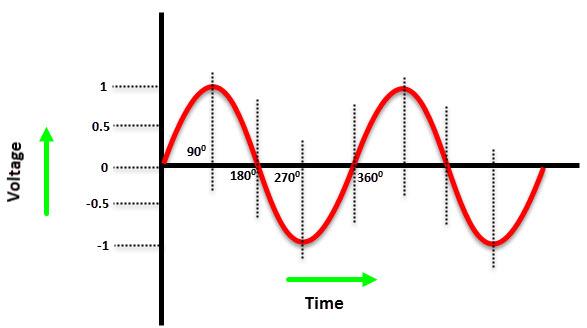
The phase wire delivers current to the load, and the neutral wire provides Return path for current. Typically, single phase voltage is 23°V and frequency is 5°Hz (it depends on where you live).
Due to voltage rises and falls (peaks and dips) in single-phase power, it is not possible to deliver constant power to the load.
Advantages
Disadvantages
What is three-phase power supply?
Three-phase power consists of three power wires (or three phases). Also, depending on the type of circuit (there are two types: star and delta), you may or may not have a neutral wire. In a three-phase power system, each AC power signal is 12° out of phase with each other.
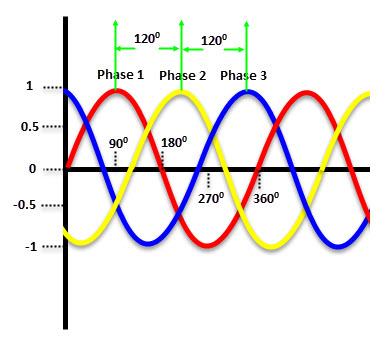
In a three-phase power supply, within a 36° cycle °, the voltage of each phase will peak twice. Additionally, power never drops to zero. This steady power flow and ability to handle higher loads makes three-phase power suitable for industrial and commercial operations.
As mentioned earlier, there are two types of circuit configurations in three-phase power supplies. They are delta and star (Y or star). In a delta configuration, there is no neutral wire, and all high voltage systems use this configuration.
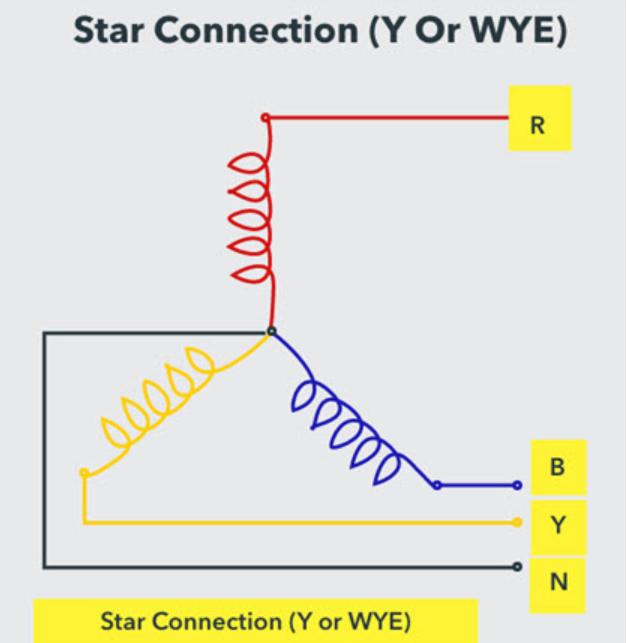
For star or star configuration, there is a neutral wire (common terminal/point of star circuit) and ground (sometimes).
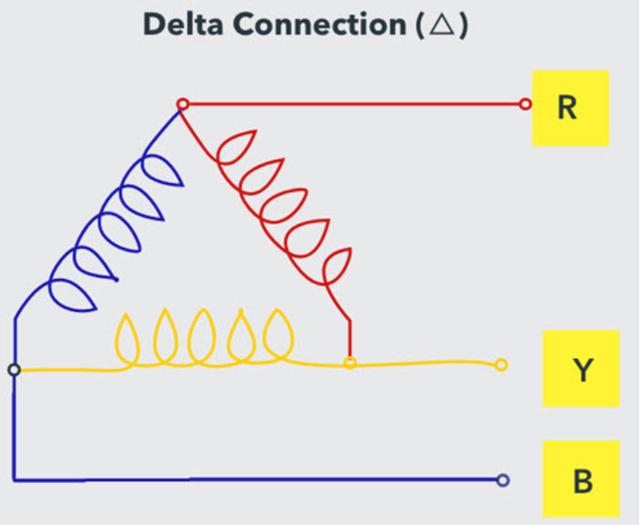
The voltage between two phases in a three-phase power supply is 415V , while the voltage between one phase and neutral is 24°V. So you can use a three-phase supply to provide three single-phase supplies (which is common practice for residential and small business loads).
Note: There is a difference between straight three-phase power and three-phase power that is split into three single-phase power supplies.
Advantage
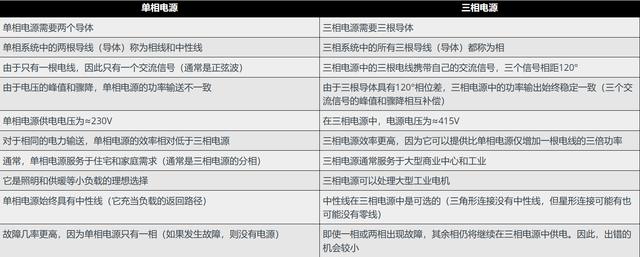
Difference Between Single Phase and Three Phase Power
Now let us see the difference between single phase and three phase power.
Comparison of Single Phase and Three Phase Power Supply
Now let us see the comparison of single phase and three phase power system in the table.
Do you need a three-phase power supply?
Depending on your requirements, your power distribution company will recommend single-phase or three-phase power. For small homes and shops, single-phase power is sufficient.
However, if you have a big house with three to four air conditioning units (all air conditioners may be running simultaneously), water heater, large submersible pump, washing machine, double door refrigerator, etc., then you may need three-phase power , so that the load of each phase is distributed correctly.
Since we don't have direct 3 phase equipment, what the distribution company does is give out the three phases of the 3 phase supply as three separate single phase supplies. For example, if you have three bedrooms and three air conditioners, each room will offer a different phase.
Apartments and communities often have dedicated transformers so that they can step down the 11kV supplied directly from the substation to 24°V without having to rely on street transformers.